- Prediction of Post-resection Prognosis Using the ADV Score for Huge Hepatocellular Carcinomas ≥13 cm
-
Shin Hwang, Ki-Hun Kim, Deok-Bog Moon, Chul-Soo Ahn, Tae-Yong Ha, Gi-Won Song, Dong-Hwan Jung, Gil-Chun Park
-
J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(1):45-57. Published online March 31, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.21.1.45
-
-
4,205
Views
-
75
Downloads
-
1
Citation
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Background/Aim
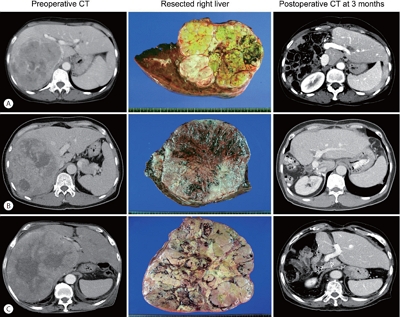
s: Multiplication of α-fetoprotein, des-γ-carboxy prothrombin, and tumor volume (ADV score) is a surrogate marker for post-resection prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This study aimed to validate the predictive power of the ADV score-based prognostic prediction model for patients with solitary huge HCC.
Methods
Of 3,018 patients, 100 patients who underwent hepatic resection for solitary HCC ≥13 cm between 2008 and 2012 were selected.
Results
The median tumor diameter and tumor volume were 15.0 cm and 886 mL, respectively. Tumor recurrence and overall survival (OS) rates were 70.7% and 66.0% at one year and 84.9% and 34.0% at five years, respectively. Microvascular invasion (MVI) was the only independent risk factor for disease-free survival (DFS) and OS. DFS and OS, stratified by ADV score with 1-log intervals, showed significant prognostic contrasts (P=0.007 and P=0.017, respectively). DFS and OS, stratified by ADV score with a cut-off of 8-log, showed significant prognostic contrasts (P=0.014 and P=0.042, respectively). The combination of MVI and ADV score with a cut-off of 8-log also showed significant prognostic contrasts in DFS (P<0.001) and OS (P=0.001) considering the number of risk factors. Prognostic contrast was enhanced after combining the MVI and ADV score.
Conclusions
The prognostic prediction model with the ADV score could reliably predict the risk of tumor recurrence and long-term patient survival outcomes in patients with solitary huge HCCs ≥13 cm. The results of this study suggest that our prognostic prediction models can be used to guide surgical treatment and post-resection follow-up for patients with huge HCCs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - ADV score is a reliable surrogate biomarker of hepatocellular carcinoma in liver resection and transplantation
Shin Hwang, Dong-Hwan Jung, Gi-Won Song
Annals of Liver Transplantation.2023; 3(2): 86. CrossRef
- Outcomes of Liver Resection and Transarterial Chemoembolization in Patients with Multinodular BCLC-A Hepatocellular Carcinoma
-
Jiwon Yang, Won-Mook Choi, Danbi Lee, Ju Hyun Shim, Kang Mo Kim, Young-Suk Lim, Han Chu Lee, Deok-Bog Moon, Dong-Hwan Jung, Jonggi Choi
-
Received March 3, 2024 Accepted March 25, 2024 Published online April 3, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2024.03.25
[Accepted]
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Background
This study aimed to compare the outcomes of liver resection (LR) and transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) in patients with multinodular hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) within the Milan criteria who were not eligible for liver transplantation.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed 483 patients with multinodular HCC within the Milan criteria, who underwent either LR or TACE as an initial therapy between 2013 and 2022. The overall survival (OS) in the entire population and recurrence-free survival (RFS) in patients who underwent LR and TACE and achieved a complete response were analyzed. Propensity score (PS) matching analysis was also used for a fair comparison of outcomes between the two groups.
Results
Among the 483 patients, 107 (22.2%) and 376 (77.8%) underwent LR and TACE, respectively. The median size of the largest tumor was 2.0 cm, and 72.3% of the patients had two HCC lesions. The median OS and RFS were significantly longer in the LR group than in the TACE group (p <0.01 for both). In the multivariate analysis, TACE (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.81 and aHR, 2.41) and large tumor size (aHR, 1.43 and aHR, 1.44) were significantly associated with worse OS and RFS, respectively. The PS-matched analysis also demonstrated that the LR group had significantly longer OS and RFS than the TACE group (PS <0.05).
Conclusion
In this study, LR showed better OS and RFS than TACE in patients with multinodular Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage A HCC. Therefore, LR can be considered an effective treatment option for these patients.
|